Hashgraph vs Blockchain: Which Technology Will Lead the Future?
Written by
Sara Illahi Panhwar
Last Updated: May 30, 2025
In this article
- Understanding blockchain: the foundation of decentralization
- What is Hashgraph? A new approach to distributed ledgers
- Hashgraph vs. blockchain
- Real-world use cases for blockchain and Hashgraph
- Key challenges and adoption barriers for both technologies
- Enterprise considerations: making the right choice
- The future of blockchain & Hashgraph: coexistence or competition?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Your Blockchain Journey Starts Here
Whether you're launching a DeFi platform, NFT marketplace or enterprise blockchain solution, we deliver technology that transforms. Book Your Free Consultation Today.
The debate of Hashgraph vs blockchain is gaining momentum in the crypto world. It mirrors the TradFi comparison of batch processing versus real-time transactions. Both Hashgraph and blockchain are distributed ledger technologies (DLTs), playing a crucial role in shaping the digital economy.
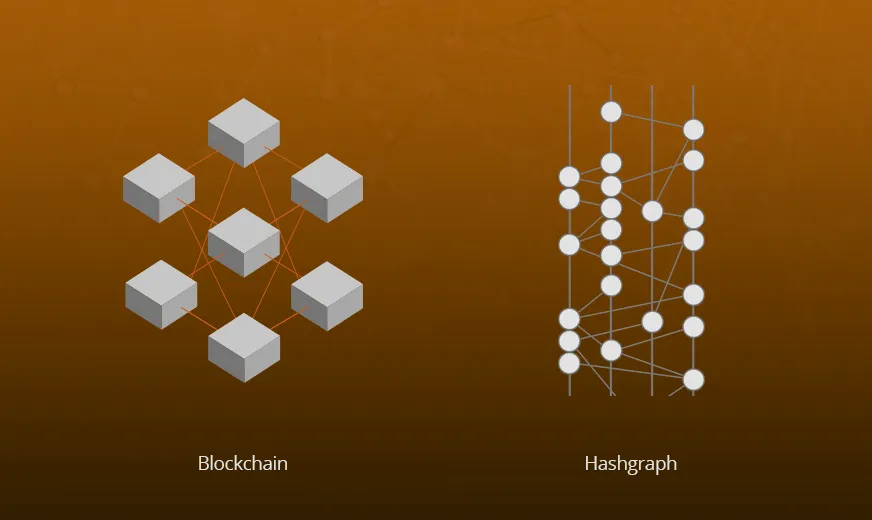
Ledgers are widely used in finance, serving as records of transactions. Various types exist, but in the crypto space, DLTs have emerged as the most significant. Among them, blockchain and Hashgraph stand out, ensuring privacy and integrity in transaction processing. While blockchain relies on a chain of blocks to store transactions, Hashgraph uses a directed graph structure to achieve the same goal.
A major debate is unfolding within blockchain-based businesses and blockchain development companies – is Hashgraph better than blockchain? This discussion stems from Hashgraph’s high speed, scalability and efficiency, while blockchain remains dominant due to its strong security and widespread adoption.
So, how do they compare? Which technology holds the advantage? What are the key use cases and implications for the future of blockchain technology? Let’s break it down.
Understanding blockchain: the foundation of decentralization
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that records transactions across a network of computers, ensuring security, transparency and decentralization. It operates on three core principles that define its functionality and reliability:
Decentralization → Unlike traditional systems that rely on a central authority, blockchain distributes transaction data across multiple nodes. This ensures that no single entity has control, making the system more resilient to manipulation or failure.
Immutability → Once recorded, data on the blockchain cannot be altered, deleted, or tampered with. This ensures transparency and trust, as every transaction remains verifiable.
Consensus mechanisms → Blockchain relies on mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) to validate transactions. These mechanisms prevent fraud and ensure that transactions are legitimate before being added to the ledger.
With the increasing adoption of blockchain, the demand for blockchain services continues to rise. The Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) market was valued at $1.90 billion in 2019, and by 2024, global blockchain spending was projected to reach $17.9 billion. Additionally, over 27% of developers worldwide are now learning or working on blockchain projects.
These figures highlight the rapid growth and significance of blockchain, as many businesses seek a blockchain development company to build scalable, secure and decentralized solutions. Giants like Microsoft and Visa have already invested heavily in blockchain technology, further solidifying its importance.
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, several of the best blockchain development trends are shaping its future:
Layer 2 scaling solutions → Addressing blockchain’s scalability challenges by enabling faster and cheaper transactions.
Modular blockchains → Enhancing flexibility by allowing developers to customize blockchain architecture to suit specific needs.
Interoperability → Improving communication between different blockchains, increasing efficiency and expanding potential use cases.
Beyond these trends, innovations such as decentralized identities (DIDs) and Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are gaining traction. These advancements are further driving blockchain’s role in transforming industries and redefining the digital economy.
What is Hashgraph? A new approach to distributed ledgers
Like blockchain, Hashgraph is an innovative distributed ledger technology (DLT) that offers a compelling alternative to blockchain. While both are used to record transactions in a decentralized manner, their underlying mechanisms differ significantly.
The primary difference between Hashgraph and blockchain lies in how they process transactions. Hashgraph utilizes parallel processing through a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG), enabling faster transaction speeds, whereas blockchain stores transactions in a linear sequence, which can sometimes result in slower processing times.
A great way to understand Hashgraph is through Hedera Hashgraph, a public distributed ledger that employs Hashgraph’s consensus mechanism. Unlike traditional blockchains, Hedera Hashgraph operates with:
Gossip-about-gossip → Nodes involved in recording and verifying transactions share data, along with details on how they received it, through a gossip protocol. This rapid communication method enables fast, efficient data distribution across the entire network.
Virtual voting → Once nodes receive transaction data, they engage in a virtual voting process to determine the final transaction order based on shared information.
These features give Hedera Hashgraph a significant edge in terms of:
Speed → Boasting an exceptionally high transactions-per-second (TPS) rate.
Fairness → Transactions are immune to manipulation, ensuring data integrity.
Efficiency → Compared to traditional consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), Hashgraph consumes less energy and operates with greater efficiency.
Hashgraph vs. blockchain
The Hashgraph vs. blockchain debate comes down to several key differences:
Consensus mechanism → One of the most fundamental differences is in how transactions are validated. Hashgraph uses gossip-about-gossip and virtual voting, whereas blockchain relies on PoW and PoS. This structural difference significantly impacts speed and efficiency.
Security → Hashgraph employs Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (aBFT), which is considered highly secure. Blockchain, while secure in its own right, follows cryptographic principles that vary depending on the type of consensus mechanism used.
Transparency and adoption → Both Hashgraph and blockchain emphasize transparency and data integrity, making them secure choices for decentralized applications. However, blockchain is far ahead in terms of adoption, with wider industry acceptance and integration.
If speed and scalability are the priority, especially for finance-related dApps or IoT-based applications, Hashgraph is the superior option due to its high throughput and efficient consensus mechanism.
If decentralization, trustlessness and transparency are more critical, blockchain is the preferred choice. These features make blockchain the backbone of cryptocurrencies, DeFi and public dApps that require maximum trust and security.
Neither technology is objectively better than the other – it all comes down to the needs of a project. Both Hashgraph and blockchain offer unique advantages, shaping the future of decentralized ledger technologies in different ways.
Real-world use cases for blockchain and Hashgraph
Blockchain use cases
1. Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies are the foundation of the blockchain ecosystem. They power decentralized networks and serve as the primary driver behind blockchain’s widespread adoption. Bitcoin and Ethereum stand as the most prominent examples, with Ethereum’s smart contracts laying the groundwork for DeFi applications. DeFi, or decentralized finance, represents the second-largest use case for blockchain, enabling lending, borrowing, staking and yield farming without intermediaries. Virtually every DeFi dApp today operates on blockchain infrastructure.
2. Supply chain management
Blockchain’s strengths in transparency, security and traceability make it an ideal tool for supply chain management. By providing an immutable record of transactions, blockchain enables businesses to track the movement of goods in real time. This level of logistical visibility reduces fraud, enhances efficiency, and ensures compliance in industries like food production, pharmaceuticals and manufacturing.
3. Smart contracts & automation
Smart contracts are among blockchain’s most transformative innovations. These self-executing agreements run on decentralized networks, automating complex processes without intermediaries. From executing financial transactions to managing legal contracts and insurance claims, smart contracts have broad applications. They streamline operations, reduce costs, and eliminate manual intervention, making automation one of blockchain’s strongest use cases.
Hashgraph use cases
1. Enterprise solutions
Businesses that require high-speed transactions and strong security frameworks can benefit significantly from Hashgraph. With its asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (aBFT) consensus mechanism, Hashgraph ensures security while maintaining fast processing speeds. This makes it particularly useful for enterprises dealing with large-scale financial operations, data verification and secure communications.
2. Digital identity & authentication
As concerns over data privacy grow, Hashgraph offers an efficient solution for establishing fraud-proof identity systems. Large corporations, governments and research institutions can use Hashgraph’s technology to verify identities, prevent identity theft and enhance security in authentication processes. The ability to manage digital identities in a tamper-proof environment is a major advantage.
3. Financial settlements
Hashgraph is well-suited for financial applications that require low-latency payments and high-speed microtransactions. This includes cross-border remittances, micro-payments and other financial activities that demand near-instant processing at minimal costs.
So, for businesses considering which technology to adopt, the decision ultimately depends on priorities.
If the focus is on decentralization, security and trustless interactions, blockchain is the preferred choice. It is widely adopted, highly resilient and supported by an extensive developer ecosystem.
If the goal is speed, efficiency and scalability, Hashgraph stands out. Its advanced consensus mechanism allows for rapid transactions while maintaining security and fairness.
Key challenges and adoption barriers for both technologies
A system without barriers and challenges only exists in an ideal environment. The real world is not ideal. Thus, blockchain and Hashgraph both have very specific challenges.
Challenges for blockchain
1. Scalability
Despite the introduction of modular chains, rollups, and Layer 2 solutions, scalability remains a work in progress for blockchain networks. As adoption grows, congestion and high gas fees continue to pose issues, requiring ongoing innovation.
2. Energy consumption
Many blockchain networks rely on Proof of Work (PoW), which is notorious for its energy-intensive operations. While Proof of Stake (PoS) significantly reduces energy consumption, PoW-based blockchains still attract criticism due to their environmental impact.
3. Regulatory uncertainty
The legal landscape for blockchain and cryptocurrencies remains unclear in many regions. Countries vary in their approach, with some embracing blockchain-friendly policies while others impose restrictions or outright bans. This lack of regulatory clarity presents a significant challenge for businesses and developers.
Challenges for Hashgraph
1. Limited adoption
Compared to blockchain, Hashgraph has yet to achieve widespread adoption. While its technology is promising, its ecosystem is not as developed, and fewer projects are currently built on it. The lack of established infrastructure and developer tools slows its mainstream acceptance.
2. Centralization concerns (Hedera Council)
Hedera Hashgraph is governed by a council of major organizations, which raises concerns about centralization. While this governance model is designed to enhance stability, critics argue that it contradicts the decentralized ethos that underpins many blockchain projects.
Enterprise considerations: making the right choice
When selecting between blockchain and Hashgraph for enterprise use, factors such as transaction speed, security and cost-efficiency come into play.
If high throughput and minimal transaction costs are the top priorities, Hashgraph is the ideal option. Its consensus mechanism allows for rapid processing, making it well-suited for high-volume applications.
If decentralization and trustless transactions are non-negotiable, blockchain remains the strongest contender. Its widespread adoption and security model provide a level of trust that businesses and consumers value.
Providers offering blockchain development services can help enterprises navigate these decisions by providing expert guidance, optimizing performance and ensuring regulatory compliance. By understanding the distinct advantages of both technologies, businesses can leverage the right distributed ledger to meet their needs.
The future of blockchain & Hashgraph: coexistence or competition?
Both blockchain and Hashgraph are still in their early stages, with significant room for growth, refinement and broader adoption. While each has its unique strengths, experts predict that both technologies will continue evolving to enhance efficiency, scalability and interoperability.
As industries increasingly adopt decentralized solutions, we can expect improvements in network performance and interconnectivity. Innovations like rollups, zero-knowledge proofs (ZK-proofs), and Layer 2 (L2) solutions will further expand blockchain’s use cases and enhance its scalability.
Another major frontier is artificial intelligence solutions, which remains in its infancy. As AI and blockchain begin to merge, they will drive mass adoption and facilitate cross-chain interoperability, breaking down existing silos between different blockchain networks.
On the other hand, Hashgraph is positioned to gain significant traction, particularly in enterprise applications. While blockchain dominates in decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs), Hashgraph has carved out a niche in corporate and institutional settings due to its speed, security, and efficiency. The future may see the rise of hybrid models or a multi-DLT ecosystem, where blockchain and Hashgraph coexist to serve different needs rather than compete directly.
Conclusion
In the end, the choice between blockchain and Hashgraph depends on specific business priorities. If decentralization and trustless interactions are paramount, blockchain remains the top choice. However, if speed, scalability and security take precedence, Hashgraph offers a compelling alternative. The best solution ultimately aligns with a company’s goals, industry requirements and long-term vision.
FAQs
1. Is Hashgraph better than blockchain? Whether Hashgraph is better than blockchain depends on individual preferences and long-term goals and needs.




